About ClO2
WHO Recommended Safe and Effective Disinfectant Used for 30+ Years
What Is Chlorine Dioxide(ClO2)?
| Name: Chlorine Dioxide | Molar Mass: 67.46 |
| Molecular Formula: ClO2 | CAS log in No.: 10049-04-4 |
| Density: 3.09(11℃) | Water-solubility: easily dissolve in water |
| Melting Point(℃): -59.5 | Boiling Point(℃): 11 |
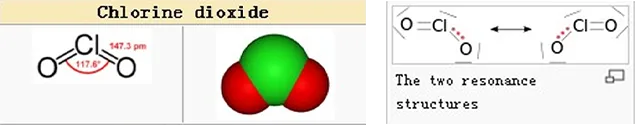
Chlorine dioxide is an oxidizing yellowish-green gas above 11℃. It has high water solubility.- approximately 10 times more soluble in water than chlorine. ClO2 does not hydrolyze when it enters water. It remains a dissolved gas in solution.
ClO2 is a powerful disinfectant that reacts rapidly via oxidation to achieve effective microbiocidal effects. It has broad spectrum performance against bacteria, fungi, algae, viruses, and parasitic microorganisms. ClO2 kills vegetative microorganisms and effectively deactivates sporulated species quickly at a low dose level.
ClO2 rapidly inactivates waterborne viruses like Rotavirus and can also be used to kill both Giardia cysts and Cryptosporidium oocysts. In industrial applications it is very effective against Sulfate Reducing Bacteria, SRB's, and Acid Producing Bacteria, APB's.
In its primary role as a disinfectant, ClO2 disrupts critical cell physiological functions, such as protein synthesis and cell membrane permeability. As a dissolved gas, ClO2 can diffuse through the cell membrane and react selectively with cellular components, such as amino acids (cysteine, tryptophan and tyrosine), viral capsids, and assembly proteins. The oxidation mechanism targets disulfide bonds in amino acids, and this results in damage to the tertiary and quaternary protein structures as well as alteration of the outer cell membrane.
The collective damage that results from this multi-faceted cellular attack makes ClO2 both broad spectrum and efficacious at very low dose rates.
Being an oxidizer, ClO2 also readily oxidizes chemicals such as sulfide, ferrous iron, dissolved manganese ions, and organic molecules with electron-rich groups. However, many organic molecules are not easily oxidized by ClO2. Consequently, chlorine dioxide minimizes wasteful reactions with organic molecules in contrast to more aggressive, less selective oxidizers.
This conserves ClO2 for its intended disinfection and/or targeted oxidation purposes, thus promoting lower application dosages and lower generation of toxic by-products versus other non-in-kind chemistries.
Surviving microorganisms can alter their structure to develop immunity to conventional biocides. In such cases continuing treatment requires a shock with higher and higher dosages or alternating biocidal chemistries. This is not known to occur with ClO2 treatment.
Chlorine dioxide is different from traditional oxidizers such as hypochlorite and other oxidizers that are ionized molecules in solution. Chlorine dioxide is a dissolved gas in solution. Therefore, it easily penetrates polysaccharide biofilms and the microbial cell wall via diffusion and performs its oxidative function on the metabolic biochemical components of the microbe. ClO2 can damage the inner membrane, denatures cellular proteins and disable the RNA. These reactions with cellular biomolecules result in impairment or death of the microorganism. The collective damage from this multifaceted attack prevents the microorganism from developing resistance and makes ClO2 both broad spectrum and efficacious at a low dose.
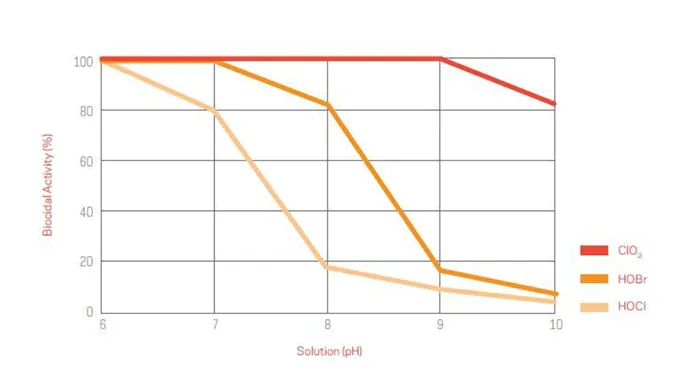
ClO2 is dissolved gas-in-solution, it does not hydrolyze into ions. Thus ClO2 can maintain its oxidative and biocidal properties over a broad pH range—from 4 to 10. This characteristic is contrary to chlorine which has a narrow pH efficacy range and are relatively ineffective antimicrobials in alkaline pH environments.
Is Chlorine Dioxide Similar to Chlorine?
No, chlorine dioxide is totally different from chlorine although there is a word “chlorine” in it.
First, chlorine dioxide ClO2 does not chlorinate organic molecules as does chlorine.
Chlorine can react by addition or substitution reactions, which incorporates a chlorine atom into an organic compound. This leads to the formation of harmful chlorinated disinfection byproducts such as trihalomethanes (THMs), chloroform, bromoform and dioxins. These halogenated DBPs are coming under increasing regulatory pressure around the globe.
Chlorine Dioxide, on the other hand, does not produce halogenated DBPs from the oxidized compound.
ClO2 only reacts with substances that give up electrons in true redox reactions. Therefore, ClO2 functions as a highly selective oxidant when it reacts with organic compounds, because it only attacks electron-rich bonds in the organic compounds. In true oxidation the organic give up electrons to the chlorine dioxide molecule. This significantly reduces the formation potential of halo acetic acid precursors, such as aldehydes, ketones and ketoacids, which then lowers the potential for THM formation in finished treated drinking water.
Second, chlorine dioxide is a five electron oxidizer and on a per weight basis provides 2.6 times the oxidative capacity of chlorine.
Third, chlorine dioxide maintains its oxidative properties over a broad pH range from various acidic environments below pH 4 to basic environments of pH 10.
Chlorine, on the other hand, has a narrow pH efficacy range and is a relatively ineffective antimicrobial in alkaline environments.
What’s The By-product of Chlorine Dioxide After Disinfection?
ClO2– + 4 R(e-) → Cl– +O2
These reactions illustrate that ClO2 can be reduced to chloride ion, and, that during this reaction process, it accepts five electrons. Chloride ion is the most ubiquitous ion in the earth's environment. A similar amount of chloride ion will be returned to the environment as administered from the ClO2 dose applied.
ClO2– + 4 R(e-) → Cl– +O2
These reactions illustrate that ClO2 can be reduced to chloride ion, and, that during this reaction process, it accepts five electrons. Chloride ion is the most ubiquitous ion in the earth's environment. A similar amount of chloride ion will be returned to the environment as administered from the ClO2 dose applied.
What Are The Chlorine Dioxide Applications?
Chlorine Dioxide Products are widely used as water purification chemicals, disinfectant, deodorizer, fungicide and preservative in a variety of industries.
Treatment of Potable Water for Human Consumption
Water Storage Systems Aboard Aircraft, Boats And Family Water Tanks
RV’s and Off‐Shore Oil Rigs
RV’s and Off‐Shore Oil Rigs

Cooling and process water microbiological control
Wastewater disinfection
Cooling Towers bio-film removal
Treatment of Ventilation Systems
Odour control
Iron and manganese removal
Paper & pulp
Influent Water Disinfection
Iron Control
Bleaching of specialty papers
Oil & gas
Microbiological control of oil wells and bores
Sulphide destruction
Pipeline and tank cleaning
THM control

Treatment of Poultry Drinking Water
Remove biofilm in water pipelines
Disinfection of Animal Confinement Facilities
Treatment of Animal Transport Vehicles
Deodorization of Animal Holding Rooms, Sick Rooms and Work Rooms
Control of Odor and Slime Forming Bacteria in Animal Confinement Facilities
Disinfection of Poultry Chiller Water / Carcass Spray
Treatment of Egg Room
Treatment of Hatching Room
Treatment of Incubator Room
Treatment of Tray Washing Room and Loading Platform
Treatment of Chick Room, Chick Grading Box and Sexing Room
Hand Dip for Poultry Workers
Shoe Bath Use

Fish and shrimp ponds daily disinfection and algae removal
Disease prevention treatment
Live Fish Transport: Transport Water, Disease treatment during holding
Fish larval rearing
Prawn larval rearing
Spraying in feeds
Treatment of diseases

Sanitizing Surfaces in food & beverage plants
Sanitizing Food‐Processing Equipment
Canning Retort and Pasteurizer Cooling Water
Stainless Steel Transfer Lines, Hydrocoolers and Pasteurizer
Washing fruit and vegetables
Washing fish and seafood
Washing meat, poultry and processing equipment
Extend shelf life and freshness of non‐processed fruits and vegetables
Process water for canned and frozen packaging
Control of bacteria growth and biofouling
Control of salmonella and legionella
Disinfection lines, holding tanks and other equipment
Disinfect in beverage and water systems and lines
Reduction of ammonia nitrogen concentration in recycled water
Cleansing and rinsing of bottles
Disinfect in beverage and water systems and lines
CIP (Cleaning In Place)

Horticulture
Greenhouse sanitation
Soil disinfection
Disinfection of irrigation water
Cleaning of irrigation system
Treatment of Agricultural Storage Facilities
Treatment of Horticulture Work Area and Benches
Treatment of Horticulture Pots and Flats
Treatment of Horticulture Cutting Tools
Treatment of Horticulture Bulbs
Treatment of Greenhouse Glass, Walkways and Under Benches
Treatment of Evaporative Coolers
Treatment of Retention Basins and Ponds
Treatment of Decorative Pools, Fountains and Water Displays
Vegetables & fruit washing/processing

Air & Surfaces Sterilization/Deodorization At Public Places and Home
Hospitals, restaurants, stations hotels air & surfaces sterilization
Lower risks of virus spreading during epidemic period
Deodorization in cars
Deodorization at toilets
Remove mould for house by the sea
Does ClO2 get approvals in world?
Chlorine Dioxide had got approvals in many countries in different applications
| Approval Time | Country | Approval Authority | Range of Application |
| 1992 | / | WHO | Drinking Water Disinfection |
| 1987 | Germany | / | Drinking Water Disinfection |
| 1985 | America | FDA | Food Processing Equipment Disinfection |
| 1987 | America | EPA | Disinfection for Food Processing Factory, Beer Brewery, Restaurant, Hospital, etc |
| 1989 | America | EPA | Disinfection for Store Water and Animal Shelters |
| 1988 | Japan | Ministry of Health | Drinking water Disinfection |
| 1987 | Australia | Ministry of Health | Food Additives, Food Bleaching Agents |
| 1987 | China | Ministry of Health | Disinfection for Food Industry, Medical, Pharmacy, Livestock, Aquaculture, Public Environment, etc. |
| 1996 | China | Ministry of Health | Food Additives for Aquatic and Fresh Products |
| 2002 | America | FDA | Disinfection for Food Processing Equipment, Pipes, Milk Processing Plants |
| 2005 | China | Ministry of Health | Drinking Water Disinfection |
| Its safety is regarded as A1 level by the world health organization(WHO) and Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) | |||
EPA APPENDIX FOR Chlorine Dioxide
| Use Site | Method of Application | Application Rate | Use Limitations |
| Agricultural Storage Facilities (Containers, Trailers, Rail Cars, Vessels) | FoamingWand | One quart to system that delivers 4-6 gallons per minute of dilution water 10 minutes contact time | Preclean with water to remove debris and dirt. |
| Mushroom Facilities: (food Contact) Stainless Steel Tanks, Transfer Lines, On-line Equipment, Picking Baskets | Flush equipment with sanitizing solution | Use-solution calls for 100-200 ppm total available chlorinedioxide | Clean equipment and surfaces thoroughlyusing a suitable detergent and rinse with water before sanitizing. |
| Disinfection of AnimalConfinement Facilities (Poultry Houses, Swine Pens, Calf Barns and Kennels | Use Commercial sprayer to saturate all surfaces | Working Solution containing 300 to 500 ppm available Chlorine Dioxide | Remove all animals and feed from premises. Remove all litter and manure from premises of facilities. Empty all troughs , racks and other feeding equipment/watering appliances.Thoroughly clean all surfaces with soap and detergent and rinse with water. |
| Poultry House Disinfection: Poultry Chiller Water/Carcass spray | Dip Carcass | 0.5 to 3 ppm for Chiller Water 70 ppm for Carcass Spray | None stated |
| Poultry Drinking Water | Add to water | 5ppm for fouled water 0.5 to 1.0ppm for control | None stated |
| Chick Room, Chick Grading Box an Sexing room | Fogger, Mop | 1,000 ppm w/ fogger 390 ppm to mop floors | None stated |
| Rention Basins and Ponds | Add to Basin | 4-9 fl oz. per 100 gallons/ 2 to 5 ppm | Do not use where fish are present |
| Decorative Pools, Fountains and Water Displays | Add to Pools | 9-18 fl oz per 100 gallons/ 5 to 10 ppm | Do not use where fish are present. |
| Food Processing Plants (Poultry, Meat, Fish) Food Contact Surface Sanitizer | 1 minutecontact time | Chlorine Dioxide 50 ppm-100 ppm | Preclean and rinse equipment. Do not reuse solution. Do not rinse treated surface |
| Process Water for Vegetable Rinses, Tanks Lines | Chemical Feed Pump or injector system | 5 ppm | Preclean all tanks, flumes and lines withsuitable detergent. |
| Potable Drinking Water | Metering Pump 1 mg/ liter (1ppm) or less 1 gallon per 100,000 gallons of treated water | 1 mg/ liter (1ppm) or less 1 gallon per 100,000 gallons of treated water | None Stated |
| Municipal Well Waters | None stated | 1 ppm | None Stated |
| Hospitals,laboratories and Institutions Hard Non Porous surfaces (Tile Floors, Walls and Ceilings and Stainless Steel Cold Rooms) | Spray, Mop or sponge | Working Solution containing 300 to 500 ppm available Chlorine Dioxide | Clean all surfaces with a suitable detergent and rinse with water prior to disinfection. |
| To Deodorize Animal Holding Rooms, Sick Rooms, Morgues and Work rooms | Spray solution on to walls ceilings and floors | Working Solution containing 1,000 ppm available chlorine dioxide | Rooms to deodorize should be ina clean condition prior to autoclaving. |
| Swimming Pools | Meetering Pump | 1 to 5ppm | None Stated |
| Recirculating Cooling Water systems | 5-20ppm | / | None Stated |

WHO & FAO Recommend ClO2 as 4th generation safe and green disinfectant to the world
ClO2 solution won't cause influence to human body under 500ppm. Common dosage is much lower as ClO2 has high effectiveness. For example 1-2ppm can kill 99.99% virus and bacterial in drinking water. ClO2 won't generate CHCl3 in disinfection process.
So it is globally recommended as the the fourth generation disinfectant after calcium hypochlorite, NaDCC and TCCA.
Please leave your request for any product you wish. We will be happy to search it for you in our databases or offer its custom synthesis.